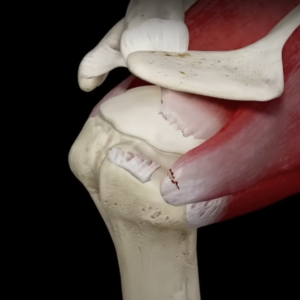
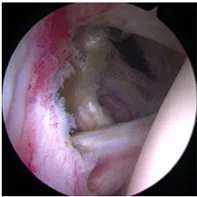
The rotator cuff is a group of four tendons wrapped around the shoulder joint like a cuff. In addition to stabilizing the joint, it also provides the strength to perform various functions. It can get affected with inflammation (tendonitis) or a tear. A rotator cuff tear is a common condition which can happen following an injury, orcan be related to wear and tear. It can cause pain, restricted movement and weakness in the shoulder joint. It can sometimes cause arthritis (rotator cuff arthropathy).
Most of the time, it can be treated non-operatively with painkillers, physiotherapy, and steroid injection. Ifsymptoms are not improving you will be advised surgical treatment, this can range from arthroscopic surgery such as a rotator cuff repair, superior capsular reconstruction or a joint replacement. Your specialist will recommend you surgery in the case of an acute tear, or for young or active patients.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is rotator cuff tear?
What causes rotator cuff tear?
- injury – road traffic accidents or sports injury
- degeneration or wear and tear in the tendon – overuse, age > 40 years, professions such as carpenter or painter
How common is rotator cuff tear?
The rotator cuff tear is relatively common, esp in elderly patients due to wear and tear. Few people may not be even aware of the tear in their tendon as they would be absolutely asymptomatic or would have very mild symptoms.
What are the symptoms?
Few patients will have compensation from the other muscles, and they will be all fine. While in others, it can cause varying degree of symptoms including
- pain in the shoulder especially while performing overhead activity or lifting heavy weights.
- night pain
- difficulty in shoulder movements too and limit function.
- weakness in shoulder with inability to lift arm
In the long term, it can cause arthritis (Rotator cuff arthropathy) when it becomes severely painful and cause further deterioration of movement and overall function.
How is rotator cuff tear diagnosed?
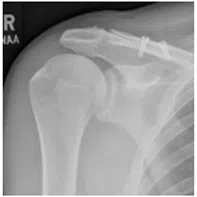
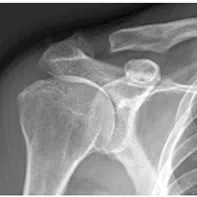
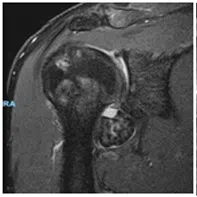
The plain X ray can show some indirect evidence of rotator cuff disease. The tear is usually confirmed with ultrasound scan or MRI scan.
How is it treated?
The treatment options for this condition include
- Physiotherapy
- Painkillers
- Injections
- surgery
The treatment is individualized based on the nature of the symptoms or the demands of the patients. Usually, the non-operative treatment options are tried first, before recommending surgery.
Do I have to have surgery?
No, good proportion of patients improve well with non-operative options who then don’t need surgery. It depends on how well other muscles compensate for the torn tendons. If you do not improve with non-operative measures, you will be considered as candidate for surgery.
What are my surgical options?
The most common surgery performed for rotator cuff tear is surgical repair of rotator cuff tendon which is done through key-hole surgery (Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair). In some occasions if the tear is large in size or the tendon is of very poor quality, you may need other procedures such as superior capsular reconstruction (SCR) or a tendon transfer (Lower trapezius transfer) or a joint replacement procedure (Reverse shoulder arthroplasty).
To know more about arthroscopic rotator cuff repair, please go to ‘Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair’ in ‘Treatments’ section.
-

Rotator cuff Tear
-
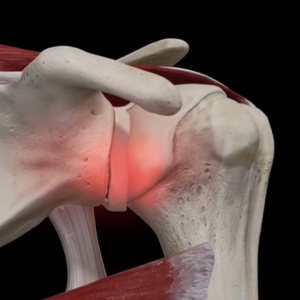
Shoulder Instability or dislocation or labral tear
-
SLAP tear
-
Shoulder arthritis
-
Acromio-clavicular joint arthritis
-
Acromio-clavicular joint dislocation
-
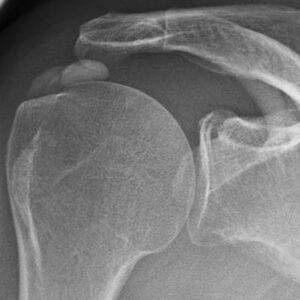
Calcific tendinitis
-
Frozen shoulder
-
Biceps tendonitis or Proximal biceps rupture
-
Shoulder Impingement
-

Pectoralis major tendon tear
-
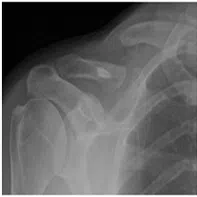
Collarbone (Clavicle) fracture
-
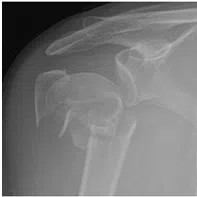
Upper arm bone (Humerus) fracture
-
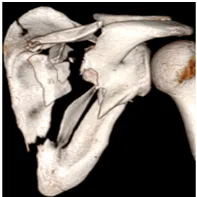
Shoulder blade (Scapula or Glenoid) Fracture
-
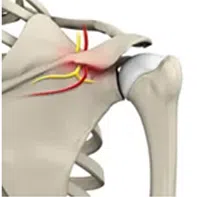
Suprascapular nerve compressive neuropathy or entrapment
-
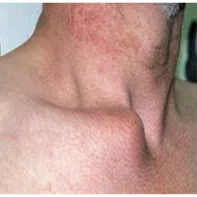
Sterno-clavicular joint instability
-
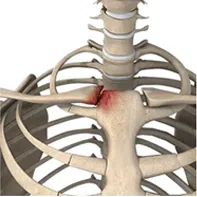
Sterno-clavicular joint arthritis
-
Snapping scapula syndrome
-
Scapula dyskinesis
-
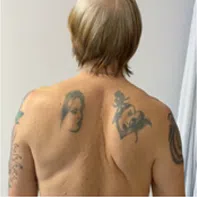
Winged scapula
-
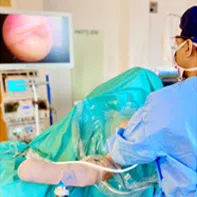
Shoulder arthroscopy
-
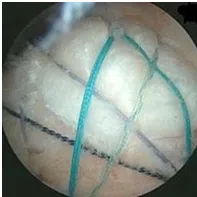
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
-
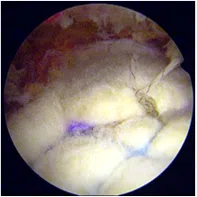
Superior capsular reconstruction
-
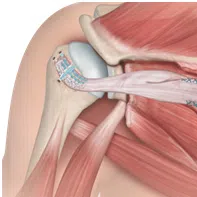
Tendon transfer
-
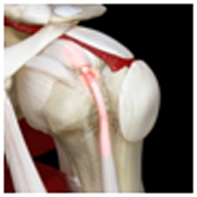
Biceps tendonitis or Proximal biceps rupture
-
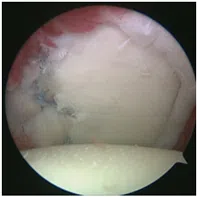
Labral repair – Bankart/ Posterior labral repair
-
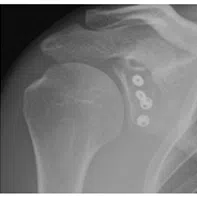
Arthroscopic latarjet
-
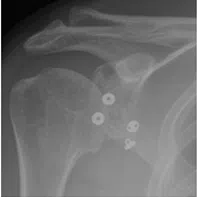
Arthroscopic bone block procedure (anterior/ posterior)
-
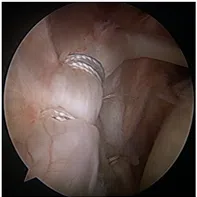
SLAP repair
-
Arthroscopic excision of calcific deposits
-
Arthroscopic capsular release
-
Arthroscopic ACJ repair/ reconstruction
-
Arthroscopic distal clavicle excision
-
Comprehensive arthroscopic management (CAM)
-
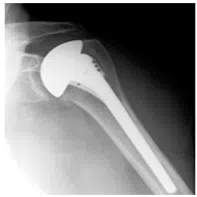
Hemiarthroplasty
-
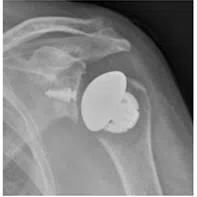
Total anatomic shoulder replacement
-
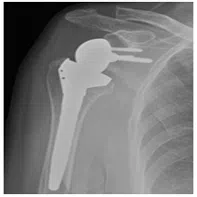
Reverse shoulder replacement
-
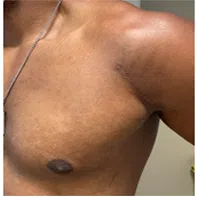
Pectoralis major tendon repair
-
Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) clavicle
-
Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) humerus
-
Arthroscopic supraspinatus nerve decompression
-
Sterno-clavicular joint procedures (Excision or Reconstruction)
-
Scapulothoracic arthroscopy
-
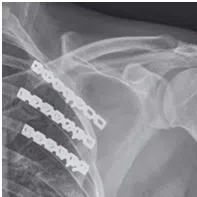
Scapulothoracic fusion
-
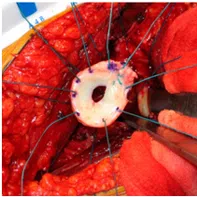
Biologic resurfacing of glenoid
-
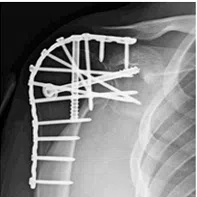
Glenohumeral fusion