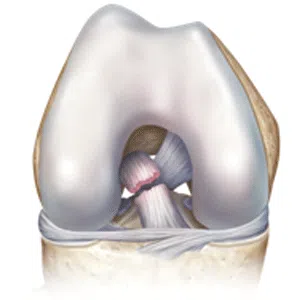
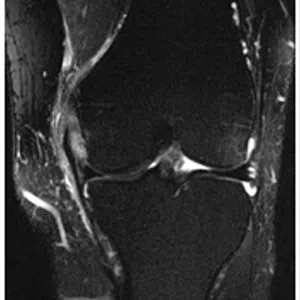
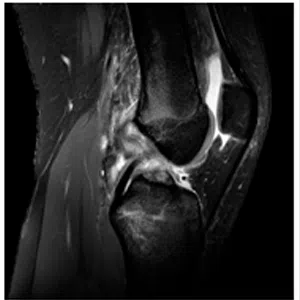
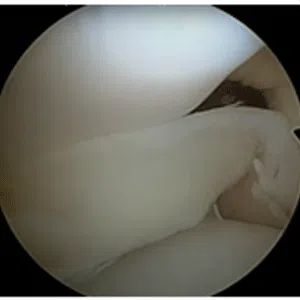
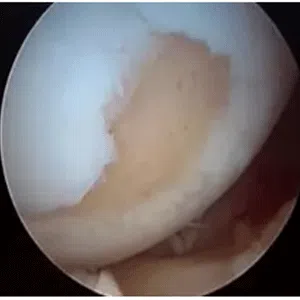
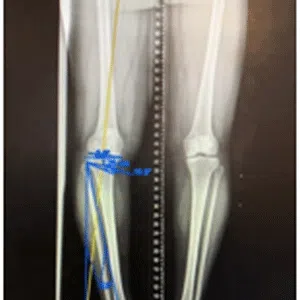
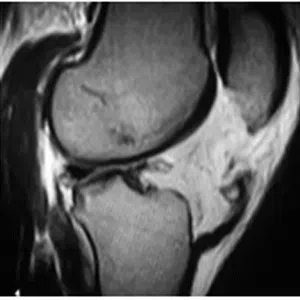
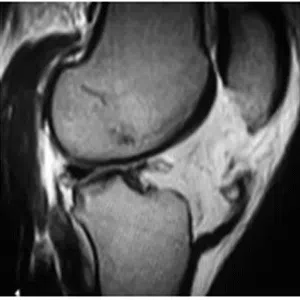
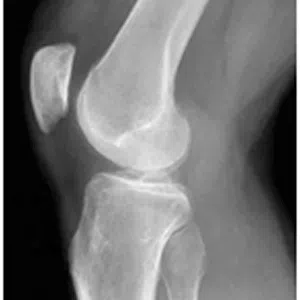
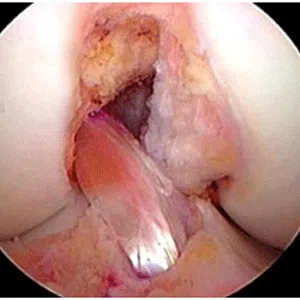
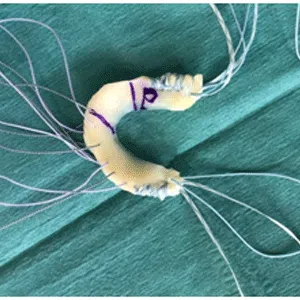
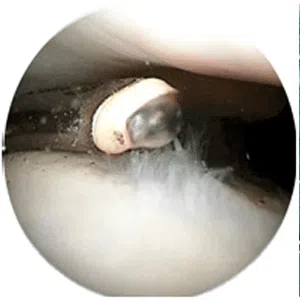
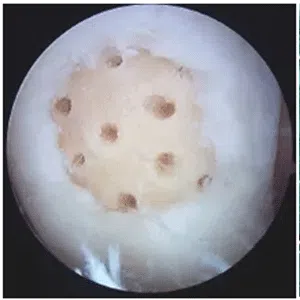
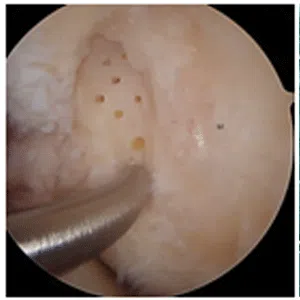
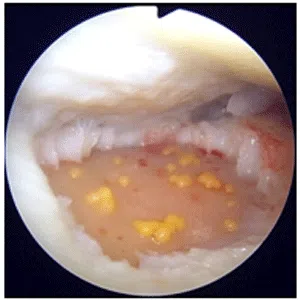
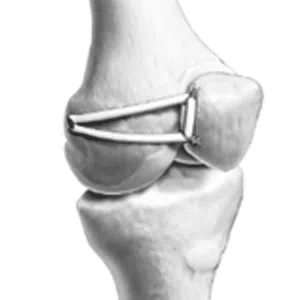
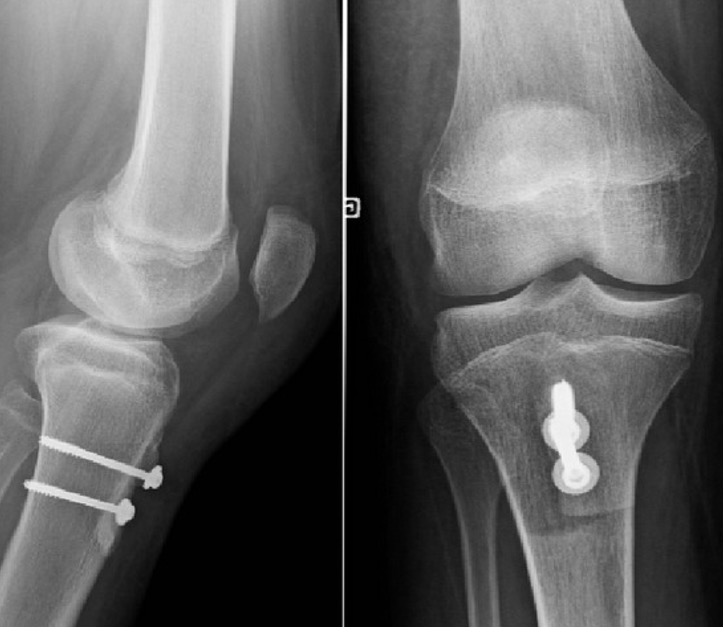
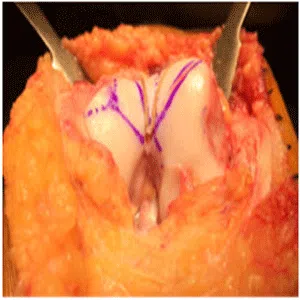
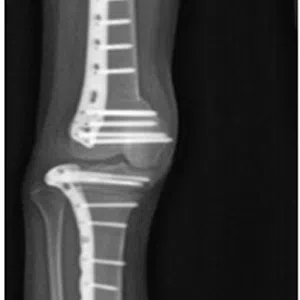
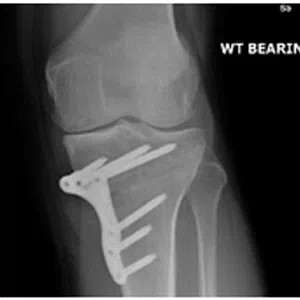
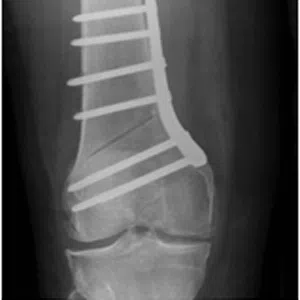
A meniscus root tear is different from a typical meniscus tear because it affects the root of the meniscus, which is the area where the meniscus is anchored to the knee joint. As a result, a meniscus root tear can cause significant instability and pain in the knee.
Meniscus root tears typically occur as a result of a traumatic event, such as a twisting injury, a direct impact, or a fall. Symptoms of a meniscus root tear can include knee pain, swelling, difficulty walking, and a feeling of instability in the knee. In some cases, a “pop” or “snap” may be felt at the time of injury.
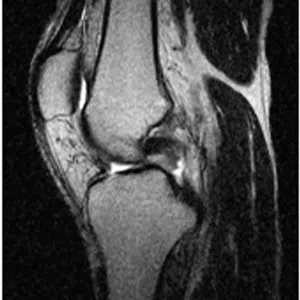
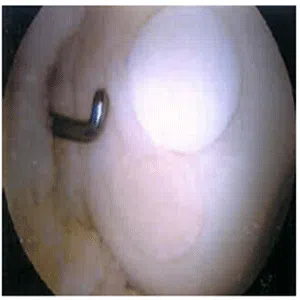
Diagnosis of a meniscus root tear typically involves a thorough evaluation by a medical professional, including a physical examination and imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scan. In some cases, a knee arthroscopy may be necessary to accurately diagnose a meniscus root tear and determine the extent of the damage.
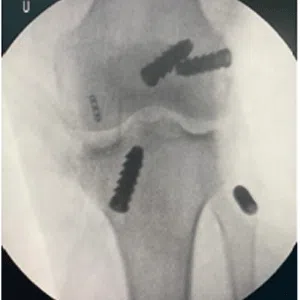
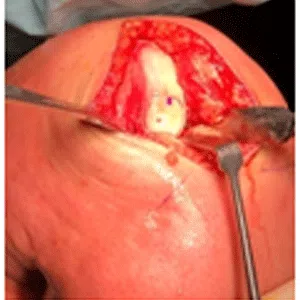
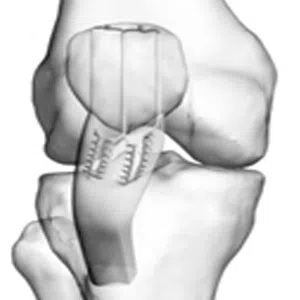
Treatment for a meniscus root tear depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s age, activity level, and overall health. In many cases, conservative management with physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises may be sufficient to manage symptoms and restore stability to the knee. However, in more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to reattach the meniscus root to its location.
The rehabilitation process after a meniscus root tear or surgery is a critical component of recovery. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are essential to regain strength, flexibility, and stability in the knee. These exercises may include range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and balance and stability training. A physical therapist can work with the patient to develop a personalized rehabilitation plan to help them progress and reach their goals.
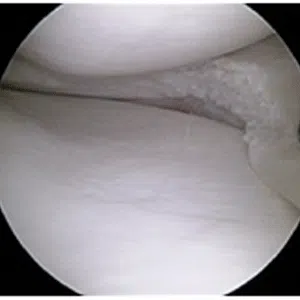
Meniscus root tear can be a painful and debilitating condition that affects the stability and function of the knee. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to manage the symptoms of a meniscus root tear and regain full function of the knee. Whether through conservative management or surgical intervention, physical therapy and rehabilitation are key to a successful outcome.
-
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear revision
-
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tear
-
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury
-
Multi-ligament tear
-
Meniscus tear
-
Meniscus root tear
-
Cartilage injury – repair/ osteochondritis dissecans
-
Knee deformity or malalignment – varus/ valgus/ rotational
-
Patellar tendon tear
-
Quadriceps tendon tear
-
Patellofemoral instability
-
Patellofemoral arthritis
-
Knee arthritis in young
-
Knee arthritis
-
Failed primary total knee replacement
-
Joint preservation surgery
-
Arthroscopic ACL repair/ reconstruction/ Revision ligament reconstruction
-
Arthroscopic PCL reconstruction
-
Multi-ligament reconstruction
-
Meniscus surgery –partial meniscectomy/ repair (root tear/ rim lesion)
-
Meniscus transplant
-
Chondroplasty
-
Microfracture
-
Nanofracture
-
BMAC
-
Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI)
-
Osteochondral Autologous Transfer Surgery (OATS) or mosaicplasty
-
Osteochondral allograft transplant
-
Patellar tendon repair/ quadriceps tendon repair
-
MPFL reconstruction
-
Tibial tuberosity transfer
-
Trochleoplasty
-
De-rotation or rotational osteotomy (Proximal tibial/ Distal femur)
-
High tibial osteotomy
-
Distal femoral osteotomy
-
Patellofemoral joint replacement
-
Total knee replacement