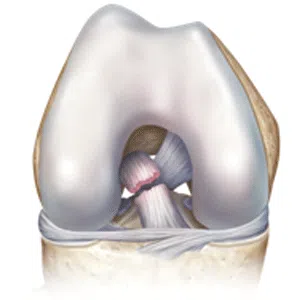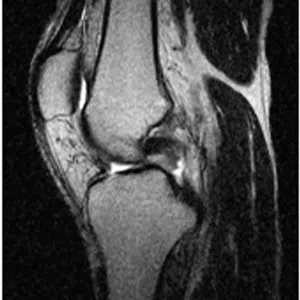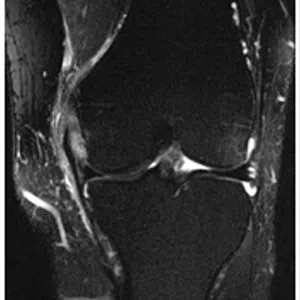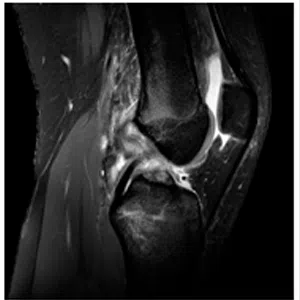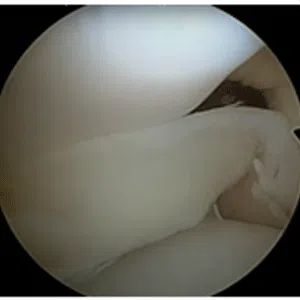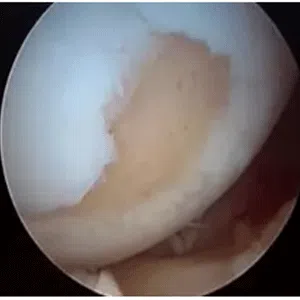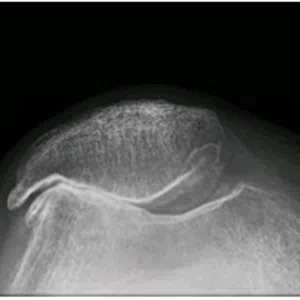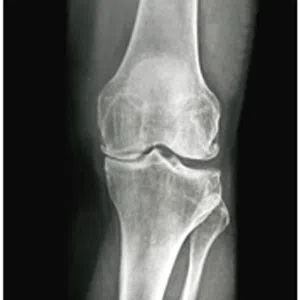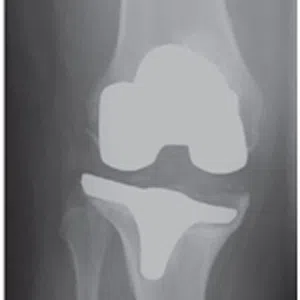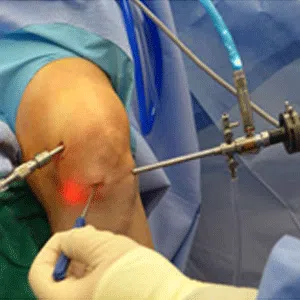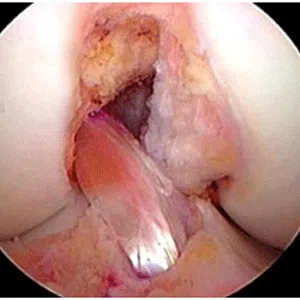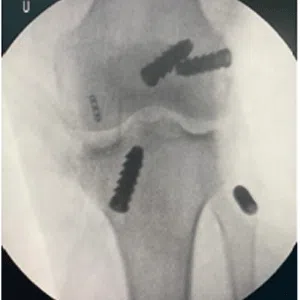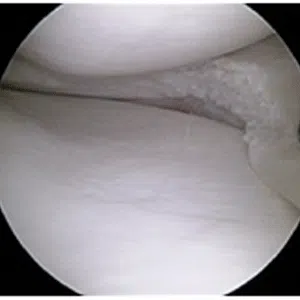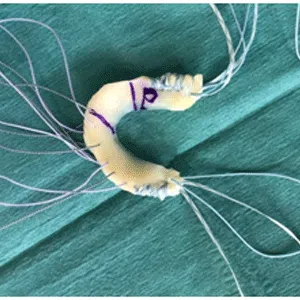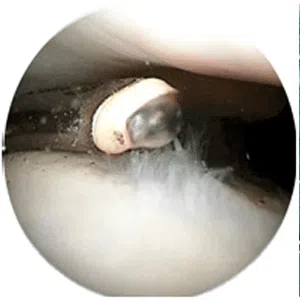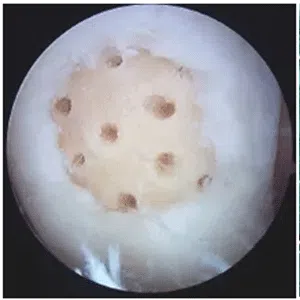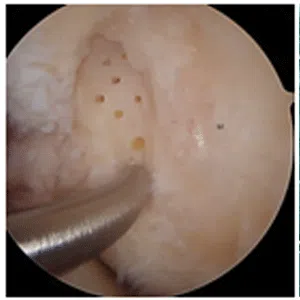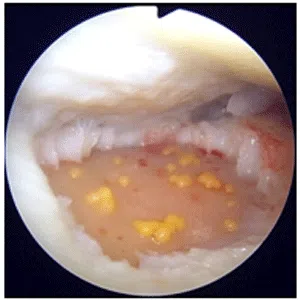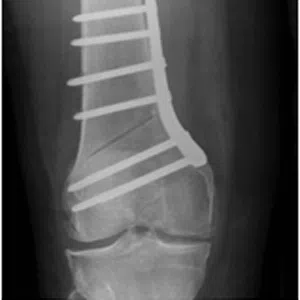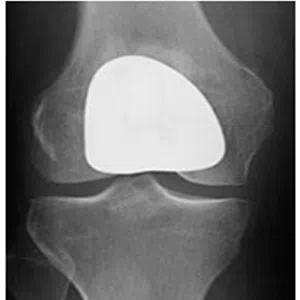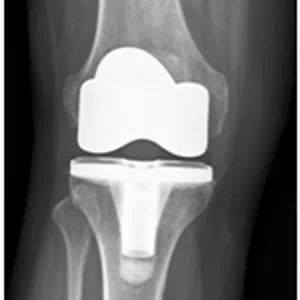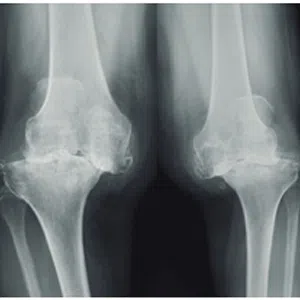
Knee arthritis in general terms is wear and tear of the cartilage inside the knee joint. Cartilage is a very smooth structure which lines the bones in the joint. It helps to reduce friction when we move the joints. Any damage to this cartilage can lead to arthritis. Cartilage is a very specialized structure inside the body. It does not however have a blood supply and therefore any repair process after injury or damage is very limited.
Cause
Arthritis is often the result multiple causative factors. However, the most common factors include:
- Age related arthritis (Osteoarthritis), Osteoarthritis is a common degenerative condition that occurs when the cartilage in the knee joint wears away and the internal environment of the knee is altered, leading to pain. Treatment of early osteoarthritis with mild symptoms includes pain relieving medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, weight loss, knee braces, and assistive devices (walking stick). In moderate disease, joint injections can be tried. For severe pain and complete loss of joint space on radiographs, knee replacement surgery (Total Knee Replacement or Partial Knee Replacement) is the treatment of choice. More and more people are presenting to doctors with symptoms of arthritis due to increased life span and improved medical care.
- Trauma (Post-traumatic arthritis), Fractures, dislocations or ligamentous injuries affecting a joint can often lead to injury to the cartilage in that joint. Over time, this progresses to cause frank arthritis, the treatment for which is usually a Total Knee Replacement surgery.
- Malalignment, Malalignment or abnormal shape of the leg can lead to excessive loads going through one side (compartment) of the knee joint causing early cartilage wear in the knee joint.
- Inflammatory arthritis (Rheumatoid arthritis) , Rheumatoid arthritis is the most common type of inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and pain in the knee joint. Treatment may include medications to reduce inflammation and relieve pain, as well as physical therapy to help maintain joint mobility and strength. Steroid injections are also an important part of the treatment. But when symptoms become severe and the joint is completely destroyed, a Total Knee Replacement is the only option.
- Infection (Post-infection sequalae) , Infection in the knee can rapidly destroy the articular cartilage leading to disabling arthritis. Once the infection has been managed with either arthroscopic or open surgery, the only treatment that can give these patients relief from pain is Total Knee Replacement.
Symptoms
Pain and swelling of the joint are the most common symptoms. Patients also complain of stiffness or reduced movement in the joint. Often there is raised temperature around the joint. The symptoms also depend on the severity of the arthritis and the manifestations are usually mild in early stages.
Prevention
Prevention is better than cure. Cartilage does not have a blood supply and therefore its regenerating potential is very limited. Ageing is a natural process and unfortunately not much can be done to stop it. However, we can delay cartilage ageing and wear by employing a healthy lifestyle which include:
- Normal body weight – The body weight determines how much load goes through the knee joint. If you are overweight, this will lead to early arthritis. Therefore, keeping one’s body weight within normal limits is a very important prevention strategy and this can be controlled through proper diet and lifestyle modifications.
- Regular exercises – Regular exercise strengthens the muscles around the knee joint and shares the load on the knee joint.
- Proper treatment for Rheumatoid arthritis – The management of rheumatoid arthritis has seen a revolution in recent years with the availability of immunological therapy.
Treatment
Vast majority of patients with arthritis respond to Conservative measures which includes weight reduction, physiotherapy, lifestyle modifications, knee brace.
If the symptoms are severe, often an injection of steroid into the joint can be very helpful. Recently, biologic treatments in the form of PRP injections have also come up which show promising results in early arthritis. Patients who continue to have severe symptoms in spite of trying conservative/ non-operative treatment for a long time can be suitable for surgical treatment. This can include procedures like osteotomy, partial or total knee replacement.
-
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear revision
-
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) tear
-
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury
-
Multi-ligament tear
-
Meniscus tear
-
Meniscus root tear
-
Cartilage injury – repair/ osteochondritis dissecans
-
Knee deformity or malalignment – varus/ valgus/ rotational
-
Patellar tendon tear
-
Quadriceps tendon tear
-
Patellofemoral instability
-
Patellofemoral arthritis
-
Knee arthritis in young
-
Knee arthritis
-
Failed primary total knee replacement
-
Joint preservation surgery
-
Arthroscopic ACL repair/ reconstruction/ Revision ligament reconstruction
-
Arthroscopic PCL reconstruction
-
Multi-ligament reconstruction
-
Meniscus surgery –partial meniscectomy/ repair (root tear/ rim lesion)
-
Meniscus transplant
-
Chondroplasty
-
Microfracture
-
Nanofracture
-
BMAC
-
Autologous chondrocyte implantation (ACI)
-
Osteochondral Autologous Transfer Surgery (OATS) or mosaicplasty
-
Osteochondral allograft transplant
-
Patellar tendon repair/ quadriceps tendon repair
-
MPFL reconstruction
-
Tibial tuberosity transfer
-
Trochleoplasty
-
De-rotation or rotational osteotomy (Proximal tibial/ Distal femur)
-
High tibial osteotomy
-
Distal femoral osteotomy
-
Patellofemoral joint replacement
-
Total knee replacement